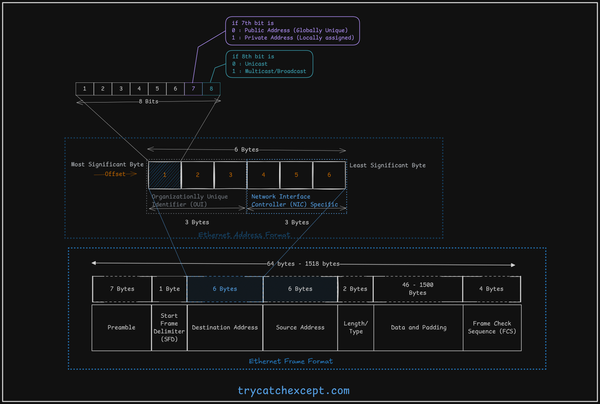
How to use Arrays?
Explaining Arrays Creating and using Arrays in C Learn C Programming
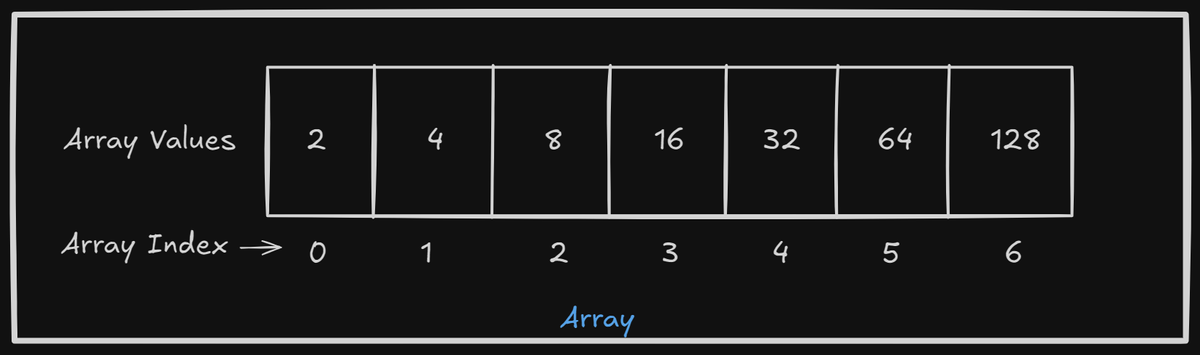
The Array is a contiguous data structure. It enables you to store data in contiguous form.
It is an indexed collection of a fixed number of homogenous type data.
Let’s assume, you want to store 5 numbers of colors in variables. Instead of storing them in each variable, you can store all the colors in an array. An array can be used anywhere, you want to store a similar type of data in a single variable.
The array is highly used when doing sorting and search operations.
For example –
//Tri Colors
const char* saffron = "#FF9933";
const char* white = "#FFFFFF";
const char* green = "#00800A"
char *tri_colors[3] = {"#FF9933", "#FFFFFF", "#00800A"};
//Iterate through first 5 prime numbers.
int prime_numbers[5] = {2,3,5,7,11};
for(int i=0; i<sizeof(prime_numbers)/sizeof(int); i++)
{
printf("%d ", prime_numbers[i]);
}tri_color
Let’s understand another example, writing a function that will return all divisors of a number.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
void get_divisors(int num, int divisors[], int arr_len)
{
int cur_index = 0;
for(int itr=1; itr<=num; itr++)
{
if(cur_index >= arr_len)
{
break;
}
if(num % itr == 0)
{
divisors[cur_index++] = itr;
}
}
}
int main()
{
int highest = 1000;
int lowest = 1;
srand ( time(NULL) );
int num = (rand() % (highest - lowest + 1)) + lowest;
int divisors[100] = {0}; // Initialize all values to zero.
get_divisors(num, divisors, 100);
printf("Divisors for (%d) - ", num);
for(int i=0; i<100; i++){
if(divisors[i] == 0)
{
break;
}
printf(" %d", divisors[i]);
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
get_divisor.c