Ethernet
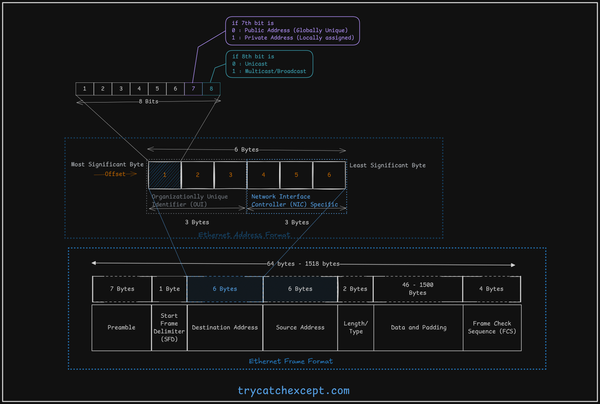
Ethernet is the world’s most widely used LAN technology, implemented in nearly 80% of LANs. It uses a bus topology and was developed at Xerox’s Palo Alto Research Center in the early 1970s. Intel, Digital and Xerox cooperated to devise a production standard, which is informally called DIX